FEV1 data comparison between Bayesian and frequentist MMRMs
2024-09-07
Source:vignettes/fev1.Rmd
fev1.RmdAbout
This vignette provides an example comparison of a Bayesian MMRM fit,
obtained by brms.mmrm::brm_model(), and a frequentist MMRM
fit, obtained by mmrm::mmrm(). An overview of parameter
estimates and differences by type of MMRM is given in the summary (Tables 4 and 5) at the end.
Prerequisites
This comparison workflow requires the following packages.
> packages <- c(
+ "dplyr",
+ "tidyr",
+ "ggplot2",
+ "gt",
+ "gtsummary",
+ "purrr",
+ "parallel",
+ "brms.mmrm",
+ "mmrm",
+ "posterior"
+ )
> invisible(lapply(packages, library, character.only = TRUE))We set a seed for the random number generator to ensure statistical reproducibility.
Data
Pre-processing
This analysis exercise uses the fev_dat dataset
contained in the mmrm-package:
It is an artificial (simulated) dataset of a clinical trial
investigating the effect of an active treatment on FEV1
(forced expired volume in one second), compared to placebo.
FEV1 is a measure of how quickly the lungs can be emptied
and low levels may indicate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
(COPD).
The dataset is a tibble with 800 rows and the following
notable variables:
-
USUBJID(subject ID) -
AVISIT(visit number, factor) -
VISITN(visit number, numeric) -
ARMCD(treatment,TRTorPBO) -
RACE(3-category race) -
SEX(female or male) -
FEV1_BL(FEV1 at baseline, %) -
FEV1(FEV1 at study visits) -
WEIGHT(weighting variable)
The primary endpoint for the analysis is change from baseline in
FEV1, which we derive below and denote
FEV1_CHG.
The rest of the pre-processing steps create factors for the study arm
and visit and apply the usual checking and standardization steps of
brms.mmrm::brm_data().
> fev_data <- brm_data(
+ data = fev_data,
+ outcome = "FEV1_CHG",
+ group = "ARMCD",
+ time = "AVISIT",
+ patient = "USUBJID",
+ baseline = "FEV1_BL",
+ reference_group = "PBO",
+ covariates = c("RACE", "SEX")
+ ) |>
+ brm_data_chronologize(order = "VISITN")The following table shows the first rows of the dataset.
> head(fev_data) |>
+ gt() |>
+ tab_caption(caption = md("Table 1. First rows of the pre-processed `fev_dat` dataset."))| USUBJID | AVISIT | ARMCD | RACE | SEX | FEV1_BL | FEV1 | WEIGHT | VISITN | VISITN2 | FEV1_CHG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT2 | VIS1 | PBO | Asian | Male | 45.02477 | NA | 0.4651848 | 1 | 0.3295078 | NA |
| PT2 | VIS2 | PBO | Asian | Male | 45.02477 | 31.45522 | 0.2330974 | 2 | -0.8204684 | -13.569552 |
| PT2 | VIS3 | PBO | Asian | Male | 45.02477 | 36.87889 | 0.3600763 | 3 | 0.4874291 | -8.145878 |
| PT2 | VIS4 | PBO | Asian | Male | 45.02477 | 48.80809 | 0.5073795 | 4 | 0.7383247 | 3.783324 |
| PT3 | VIS1 | PBO | Black or African American | Female | 43.50070 | NA | 0.6821642 | 1 | 0.5757814 | NA |
| PT3 | VIS2 | PBO | Black or African American | Female | 43.50070 | 35.98699 | 0.8917896 | 2 | -0.3053884 | -7.513705 |
Descriptive statistics
Table of baseline characteristics:
> fev_data |>
+ select(ARMCD, USUBJID, SEX, RACE, FEV1_BL) |>
+ distinct() |>
+ select(-USUBJID) |>
+ tbl_summary(
+ by = c(ARMCD),
+ statistic = list(
+ all_continuous() ~ "{mean} ({sd})",
+ all_categorical() ~ "{n} / {N} ({p}%)"
+ )
+ ) |>
+ modify_caption("Table 2. Baseline characteristics.")| Characteristic |
PBO N = 1051 |
TRT N = 951 |
|---|---|---|
| SEX | ||
| Male | 50 / 105 (48%) | 44 / 95 (46%) |
| Female | 55 / 105 (52%) | 51 / 95 (54%) |
| RACE | ||
| Asian | 38 / 105 (36%) | 32 / 95 (34%) |
| Black or African American | 46 / 105 (44%) | 29 / 95 (31%) |
| White | 21 / 105 (20%) | 34 / 95 (36%) |
| FEV1_BL | 40 (9) | 40 (9) |
| 1 n / N (%); Mean (SD) | ||
Table of change from baseline in FEV1 over 52 weeks:
> fev_data |>
+ pull(AVISIT) |>
+ unique() |>
+ sort() |>
+ purrr::map(
+ .f = ~ fev_data |>
+ filter(AVISIT %in% .x) |>
+ tbl_summary(
+ by = ARMCD,
+ include = FEV1_CHG,
+ type = FEV1_CHG ~ "continuous2",
+ statistic = FEV1_CHG ~ c(
+ "{mean} ({sd})",
+ "{median} ({p25}, {p75})",
+ "{min}, {max}"
+ ),
+ label = list(FEV1_CHG = paste("Visit ", .x))
+ )
+ ) |>
+ tbl_stack(quiet = TRUE) |>
+ modify_caption("Table 3. Change from baseline.")| Characteristic |
PBO N = 105 |
TRT N = 95 |
|---|---|---|
| Visit VIS1 | ||
| Mean (SD) | -8 (9) | -2 (10) |
| Median (Q1, Q3) | -9 (-16, 0) | -4 (-9, 7) |
| Min, Max | -26, 12 | -24, 20 |
| Unknown | 37 | 29 |
| Visit VIS2 | ||
| Mean (SD) | -3 (8) | 2 (9) |
| Median (Q1, Q3) | -3 (-10, 1) | 2 (-4, 8) |
| Min, Max | -20, 15 | -22, 23 |
| Unknown | 36 | 24 |
| Visit VIS3 | ||
| Mean (SD) | 2 (8) | 5 (9) |
| Median (Q1, Q3) | 2 (-2, 8) | 6 (0, 11) |
| Min, Max | -15, 20 | -19, 30 |
| Unknown | 34 | 37 |
| Visit VIS4 | ||
| Mean (SD) | 8 (12) | 13 (13) |
| Median (Q1, Q3) | 6 (1, 20) | 12 (5, 23) |
| Min, Max | -20, 39 | -14, 47 |
| Unknown | 38 | 28 |
The following figure shows the primary endpoint over the four study visits in the data.
> fev_data |>
+ group_by(ARMCD) |>
+ ggplot(aes(x = AVISIT, y = FEV1_CHG, fill = factor(ARMCD))) +
+ geom_hline(yintercept = 0, col = "grey", linewidth = 1.2) +
+ geom_boxplot(na.rm = TRUE) +
+ labs(
+ x = "Visit",
+ y = "Change from baseline in FEV1",
+ fill = "Treatment"
+ ) +
+ scale_fill_manual(values = c("darkgoldenrod2", "coral2")) +
+ theme_bw()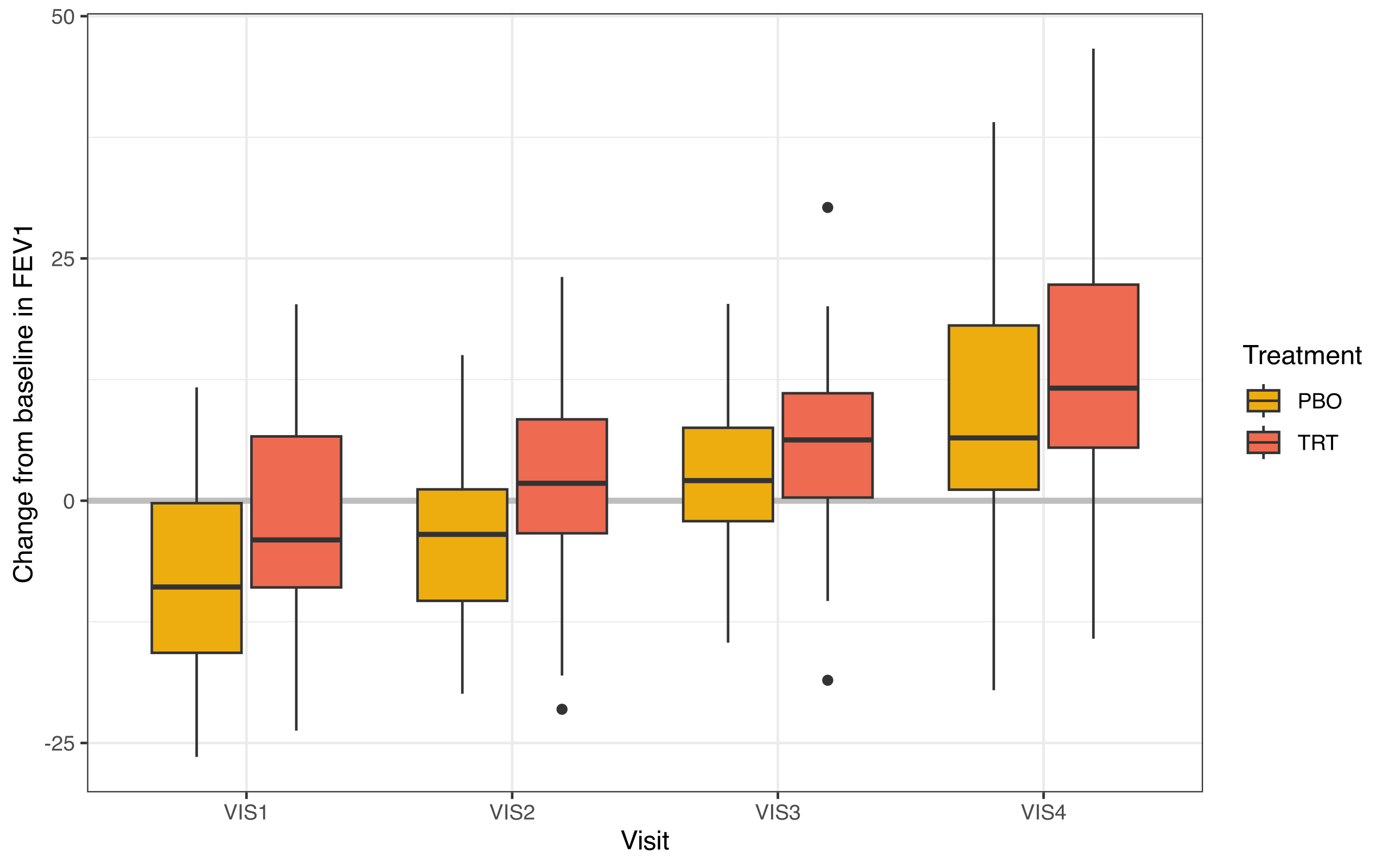
Figure 1. Change from baseline in FEV1 over 4 visit time points.
Fitting MMRMs
Bayesian model
The formula for the Bayesian model includes additive effects for baseline, study visit, race, sex, and study-arm-by-visit interaction.
> b_mmrm_formula <- brm_formula(
+ data = fev_data,
+ intercept = TRUE,
+ baseline = TRUE,
+ group = FALSE,
+ time = TRUE,
+ baseline_time = FALSE,
+ group_time = TRUE,
+ correlation = "unstructured"
+ )
> print(b_mmrm_formula)
#> FEV1_CHG ~ FEV1_BL + ARMCD:AVISIT + AVISIT + RACE + SEX + unstr(time = AVISIT, gr = USUBJID)
#> sigma ~ 0 + AVISITWe fit the model using brms.mmrm::brm_model(). To ensure
a good basis of comparison with the frequentist model, we put an
extremely diffuse prior on the intercept. The parameters already have
diffuse flexible priors by default.
> b_mmrm_fit <- brm_model(
+ data = filter(fev_data, !is.na(FEV1_CHG)),
+ formula = b_mmrm_formula,
+ prior = brms::prior(class = "Intercept", prior = "student_t(3, 0, 1000)"),
+ iter = 10000,
+ warmup = 2000,
+ chains = 4,
+ cores = 4,
+ seed = 1,
+ refresh = 0
+ )Here is a posterior summary of model parameters, including fixed effects and pairwise correlation among visits within patients.
> summary(b_mmrm_fit)
#> Family: gaussian
#> Links: mu = identity; sigma = log
#> Formula: FEV1_CHG ~ FEV1_BL + ARMCD:AVISIT + AVISIT + RACE + SEX + unstr(time = AVISIT, gr = USUBJID)
#> sigma ~ 0 + AVISIT
#> Data: data[!is.na(data[[attr(data, "brm_outcome")]]), ] (Number of observations: 537)
#> Draws: 4 chains, each with iter = 10000; warmup = 2000; thin = 1;
#> total post-warmup draws = 32000
#>
#> Correlation Structures:
#> Estimate Est.Error l-95% CI u-95% CI Rhat Bulk_ESS Tail_ESS
#> cortime(VIS1,VIS2) 0.36 0.08 0.18 0.52 1.00 48758 26086
#> cortime(VIS1,VIS3) 0.14 0.10 -0.05 0.33 1.00 49018 26172
#> cortime(VIS2,VIS3) 0.04 0.10 -0.16 0.23 1.00 49178 25472
#> cortime(VIS1,VIS4) 0.17 0.11 -0.06 0.38 1.00 49528 25555
#> cortime(VIS2,VIS4) 0.11 0.09 -0.07 0.28 1.00 49509 24007
#> cortime(VIS3,VIS4) 0.01 0.10 -0.18 0.21 1.00 45294 24353
#>
#> Regression Coefficients:
#> Estimate Est.Error l-95% CI u-95% CI Rhat Bulk_ESS
#> Intercept 24.34 1.41 21.60 27.09 1.00 43678
#> FEV1_BL -0.84 0.03 -0.89 -0.78 1.00 56286
#> AVISIT2 4.80 0.82 3.20 6.40 1.00 31792
#> AVISIT3 10.37 0.83 8.73 12.01 1.00 29808
#> AVISIT4 15.20 1.33 12.60 17.83 1.00 35293
#> RACEBlackorAfricanAmerican 1.41 0.59 0.27 2.55 1.00 46945
#> RACEWhite 5.46 0.63 4.23 6.69 1.00 47801
#> SEXFemale 0.35 0.51 -0.64 1.36 1.00 49193
#> AVISITVIS1:ARMCDTRT 3.98 1.07 1.89 6.06 1.00 31646
#> AVISITVIS2:ARMCDTRT 3.93 0.83 2.31 5.55 1.00 46665
#> AVISITVIS3:ARMCDTRT 2.98 0.68 1.65 4.31 1.00 52457
#> AVISITVIS4:ARMCDTRT 4.41 1.68 1.06 7.71 1.00 45307
#> sigma_AVISITVIS1 1.83 0.06 1.71 1.95 1.00 50344
#> sigma_AVISITVIS2 1.59 0.06 1.47 1.71 1.00 48248
#> sigma_AVISITVIS3 1.33 0.06 1.21 1.46 1.00 48058
#> sigma_AVISITVIS4 2.28 0.06 2.16 2.41 1.00 51078
#> Tail_ESS
#> Intercept 25394
#> FEV1_BL 24494
#> AVISIT2 24396
#> AVISIT3 24188
#> AVISIT4 24810
#> RACEBlackorAfricanAmerican 25405
#> RACEWhite 23816
#> SEXFemale 24919
#> AVISITVIS1:ARMCDTRT 26255
#> AVISITVIS2:ARMCDTRT 23809
#> AVISITVIS3:ARMCDTRT 24705
#> AVISITVIS4:ARMCDTRT 25026
#> sigma_AVISITVIS1 26156
#> sigma_AVISITVIS2 24526
#> sigma_AVISITVIS3 24328
#> sigma_AVISITVIS4 23975
#>
#> Draws were sampled using sampling(NUTS). For each parameter, Bulk_ESS
#> and Tail_ESS are effective sample size measures, and Rhat is the potential
#> scale reduction factor on split chains (at convergence, Rhat = 1).Frequentist model
The formula for the frequentist model is the same, except for the different syntax for specifying the covariance structure of the MMRM. We fit the model below.
> f_mmrm_fit <- mmrm::mmrm(
+ formula = FEV1_CHG ~ FEV1_BL + ARMCD:AVISIT + AVISIT + RACE + SEX +
+ us(AVISIT | USUBJID),
+ data = mutate(
+ fev_data,
+ AVISIT = factor(as.character(AVISIT), ordered = FALSE)
+ )
+ )The parameter summaries of the frequentist model are below.
> summary(f_mmrm_fit)
#> mmrm fit
#>
#> Formula:
#> FEV1_CHG ~ FEV1_BL + ARMCD:AVISIT + AVISIT + RACE + SEX + us(AVISIT |
#> USUBJID)
#> Data:
#> mutate(fev_data, AVISIT = factor(as.character(AVISIT), ordered = FALSE)) (used
#> 537 observations from 197 subjects with maximum 4 timepoints)
#> Covariance: unstructured (10 variance parameters)
#> Method: Satterthwaite
#> Vcov Method: Asymptotic
#> Inference: REML
#>
#> Model selection criteria:
#> AIC BIC logLik deviance
#> 3381.4 3414.2 -1680.7 3361.4
#>
#> Coefficients:
#> Estimate Std. Error df t value Pr(>|t|)
#> (Intercept) 24.35372 1.40754 257.97000 17.302 < 2e-16
#> FEV1_BL -0.84022 0.02777 190.27000 -30.251 < 2e-16
#> AVISITVIS2 4.79036 0.79848 144.82000 5.999 1.51e-08
#> AVISITVIS3 10.36601 0.81318 157.08000 12.748 < 2e-16
#> AVISITVIS4 15.19231 1.30857 139.25000 11.610 < 2e-16
#> RACEBlack or African American 1.41921 0.57874 169.56000 2.452 0.015211
#> RACEWhite 5.45679 0.61626 157.54000 8.855 1.65e-15
#> SEXFemale 0.33812 0.49273 166.43000 0.686 0.493529
#> AVISITVIS1:ARMCDTRT 3.98329 1.04540 142.32000 3.810 0.000206
#> AVISITVIS2:ARMCDTRT 3.93076 0.81351 142.26000 4.832 3.46e-06
#> AVISITVIS3:ARMCDTRT 2.98372 0.66567 129.61000 4.482 1.61e-05
#> AVISITVIS4:ARMCDTRT 4.40400 1.66049 132.88000 2.652 0.008970
#>
#> (Intercept) ***
#> FEV1_BL ***
#> AVISITVIS2 ***
#> AVISITVIS3 ***
#> AVISITVIS4 ***
#> RACEBlack or African American *
#> RACEWhite ***
#> SEXFemale
#> AVISITVIS1:ARMCDTRT ***
#> AVISITVIS2:ARMCDTRT ***
#> AVISITVIS3:ARMCDTRT ***
#> AVISITVIS4:ARMCDTRT **
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Covariance estimate:
#> VIS1 VIS2 VIS3 VIS4
#> VIS1 37.8301 11.3255 3.4796 10.6844
#> VIS2 11.3255 23.5476 0.7760 5.5103
#> VIS3 3.4796 0.7760 13.8037 0.5683
#> VIS4 10.6844 5.5103 0.5683 92.9625Comparison
This section compares the Bayesian posterior parameter estimates from
brms.mmrm to the frequentist parameter estimates of the
mmrm package.
Extract estimates from Bayesian model
We extract and standardize the Bayesian estimates.
> b_mmrm_draws <- b_mmrm_fit |>
+ as_draws_df()
> visit_levels <- sort(unique(as.character(fev_data$AVISIT)))
> for (level in visit_levels) {
+ name <- paste0("b_sigma_AVISIT", level)
+ b_mmrm_draws[[name]] <- exp(b_mmrm_draws[[name]])
+ }
> b_mmrm_summary <- b_mmrm_draws |>
+ summarize_draws() |>
+ select(variable, mean, sd) |>
+ filter(!(variable %in% c("Intercept", "lprior", "lp__"))) |>
+ rename(bayes_estimate = mean, bayes_se = sd) |>
+ mutate(
+ variable = variable |>
+ tolower() |>
+ gsub(pattern = "b_", replacement = "") |>
+ gsub(pattern = "b_sigma_AVISIT", replacement = "sigma_") |>
+ gsub(pattern = "cortime", replacement = "correlation") |>
+ gsub(pattern = "__", replacement = "_") |>
+ gsub(pattern = "avisitvis", replacement = "avisit")
+ )Extract estimates from frequentist model
We extract and standardize the frequentist estimates.
> f_mmrm_fixed <- summary(f_mmrm_fit)$coefficients |>
+ as_tibble(rownames = "variable") |>
+ mutate(variable = tolower(variable)) |>
+ mutate(variable = gsub("(", "", variable, fixed = TRUE)) |>
+ mutate(variable = gsub(")", "", variable, fixed = TRUE)) |>
+ mutate(variable = gsub("avisitvis", "avisit", variable)) |>
+ rename(freq_estimate = Estimate, freq_se = `Std. Error`) |>
+ select(variable, freq_estimate, freq_se)> f_mmrm_variance <- tibble(
+ variable = paste0("sigma_AVISIT", visit_levels) |>
+ tolower() |>
+ gsub(pattern = "avisitvis", replacement = "avisit"),
+ freq_estimate = sqrt(diag(f_mmrm_fit$cov))
+ )> f_diagonal_factor <- diag(1 / sqrt(diag(f_mmrm_fit$cov)))
> f_corr_matrix <- f_diagonal_factor %*% f_mmrm_fit$cov %*% f_diagonal_factor
> colnames(f_corr_matrix) <- visit_levels> f_mmrm_correlation <- f_corr_matrix |>
+ as.data.frame() |>
+ as_tibble() |>
+ mutate(x1 = visit_levels) |>
+ pivot_longer(
+ cols = -any_of("x1"),
+ names_to = "x2",
+ values_to = "freq_estimate"
+ ) |>
+ filter(
+ as.numeric(gsub("[^0-9]", "", x1)) < as.numeric(gsub("[^0-9]", "", x2))
+ ) |>
+ mutate(variable = sprintf("correlation_%s_%s", x1, x2)) |>
+ select(variable, freq_estimate)Summary
The first table below summarizes the parameter estimates from each model and the differences between estimates (Bayesian minus frequentist). The second table shows the standard errors of these estimates and differences between standard errors. In each table, the “Relative” column shows the relative difference (the difference divided by the frequentist quantity).
Because of the different statistical paradigms and estimation
procedures, especially regarding the covariance parameters, it would not
be realistic to expect the Bayesian and frequentist approaches to yield
virtually identical results. Nevertheless, the absolute and relative
differences in the table below show strong agreement between
brms.mmrm and mmrm.
> b_f_comparison <- full_join(
+ x = b_mmrm_summary,
+ y = f_mmrm_summary,
+ by = "variable"
+ ) |>
+ mutate(
+ diff_estimate = bayes_estimate - freq_estimate,
+ diff_relative_estimate = diff_estimate / freq_estimate,
+ diff_se = bayes_se - freq_se,
+ diff_relative_se = diff_se / freq_se
+ ) |>
+ select(variable, ends_with("estimate"), ends_with("se"))> table_estimates <- b_f_comparison |>
+ select(variable, ends_with("estimate"))
> gt(table_estimates) |>
+ fmt_number(decimals = 4) |>
+ tab_caption(
+ caption = md(
+ paste(
+ "Table 4. Comparison of parameter estimates between",
+ "Bayesian and frequentist MMRMs."
+ )
+ )
+ ) |>
+ cols_label(
+ variable = "Variable",
+ bayes_estimate = "Bayesian",
+ freq_estimate = "Frequentist",
+ diff_estimate = "Difference",
+ diff_relative_estimate = "Relative"
+ )| Variable | Bayesian | Frequentist | Difference | Relative |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| intercept | 24.3351 | 24.3537 | −0.0186 | −0.0008 |
| fev1_bl | −0.8399 | −0.8402 | 0.0003 | −0.0004 |
| avisit2 | 4.7996 | 4.7904 | 0.0093 | 0.0019 |
| avisit3 | 10.3730 | 10.3660 | 0.0070 | 0.0007 |
| avisit4 | 15.1989 | 15.1923 | 0.0066 | 0.0004 |
| raceblackorafricanamerican | 1.4131 | 1.4192 | −0.0061 | −0.0043 |
| racewhite | 5.4556 | 5.4568 | −0.0012 | −0.0002 |
| sexfemale | 0.3456 | 0.3381 | 0.0075 | 0.0221 |
| avisit1:armcdtrt | 3.9842 | 3.9833 | 0.0009 | 0.0002 |
| avisit2:armcdtrt | 3.9330 | 3.9308 | 0.0023 | 0.0006 |
| avisit3:armcdtrt | 2.9795 | 2.9837 | −0.0042 | −0.0014 |
| avisit4:armcdtrt | 4.4066 | 4.4040 | 0.0026 | 0.0006 |
| sigma_avisit1 | 6.2317 | 6.1506 | 0.0811 | 0.0132 |
| sigma_avisit2 | 4.9146 | 4.8526 | 0.0620 | 0.0128 |
| sigma_avisit3 | 3.7775 | 3.7153 | 0.0622 | 0.0167 |
| sigma_avisit4 | 9.7953 | 9.6417 | 0.1536 | 0.0159 |
| correlation_vis1_vis2 | 0.3607 | 0.3795 | −0.0187 | −0.0493 |
| correlation_vis1_vis3 | 0.1419 | 0.1523 | −0.0104 | −0.0683 |
| correlation_vis2_vis3 | 0.0396 | 0.0430 | −0.0034 | −0.0791 |
| correlation_vis1_vis4 | 0.1680 | 0.1802 | −0.0121 | −0.0674 |
| correlation_vis2_vis4 | 0.1110 | 0.1178 | −0.0067 | −0.0571 |
| correlation_vis3_vis4 | 0.0144 | 0.0159 | −0.0015 | −0.0929 |
> table_se <- b_f_comparison |>
+ select(variable, ends_with("se")) |>
+ filter(!is.na(freq_se))
> gt(table_se) |>
+ fmt_number(decimals = 4) |>
+ tab_caption(
+ caption = md(
+ paste(
+ "Table 5. Comparison of parameter standard errors between",
+ "Bayesian and frequentist MMRMs."
+ )
+ )
+ ) |>
+ cols_label(
+ variable = "Variable",
+ bayes_se = "Bayesian",
+ freq_se = "Frequentist",
+ diff_se = "Difference",
+ diff_relative_se = "Relative"
+ )| Variable | Bayesian | Frequentist | Difference | Relative |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| intercept | 1.4125 | 1.4075 | 0.0050 | 0.0035 |
| fev1_bl | 0.0279 | 0.0278 | 0.0001 | 0.0046 |
| avisit2 | 0.8176 | 0.7985 | 0.0191 | 0.0239 |
| avisit3 | 0.8335 | 0.8132 | 0.0203 | 0.0250 |
| avisit4 | 1.3283 | 1.3086 | 0.0198 | 0.0151 |
| raceblackorafricanamerican | 0.5857 | 0.5787 | 0.0070 | 0.0120 |
| racewhite | 0.6252 | 0.6163 | 0.0089 | 0.0144 |
| sexfemale | 0.5119 | 0.4927 | 0.0192 | 0.0390 |
| avisit1:armcdtrt | 1.0651 | 1.0454 | 0.0197 | 0.0188 |
| avisit2:armcdtrt | 0.8260 | 0.8135 | 0.0125 | 0.0154 |
| avisit3:armcdtrt | 0.6771 | 0.6657 | 0.0114 | 0.0171 |
| avisit4:armcdtrt | 1.6805 | 1.6605 | 0.0200 | 0.0120 |
Session info
> sessionInfo()
#> R version 4.4.0 (2024-04-24)
#> Platform: aarch64-apple-darwin20
#> Running under: macOS Sonoma 14.5
#>
#> Matrix products: default
#> BLAS: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.4-arm64/Resources/lib/libRblas.0.dylib
#> LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.4-arm64/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib; LAPACK version 3.12.0
#>
#> locale:
#> [1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8
#>
#> time zone: America/Indiana/Indianapolis
#> tzcode source: internal
#>
#> attached base packages:
#> [1] parallel stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods
#> [8] base
#>
#> other attached packages:
#> [1] posterior_1.5.0 mmrm_0.3.11 brms.mmrm_1.0.1.9005
#> [4] purrr_1.0.2 gtsummary_1.9.9.9003 gt_0.10.1
#> [7] ggplot2_3.5.1 tidyr_1.3.1 dplyr_1.1.4
#> [10] knitr_1.46
#>
#> loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
#> [1] tidyselect_1.2.1 svUnit_1.0.6 farver_2.1.2
#> [4] loo_2.7.0 tidybayes_3.0.6 fastmap_1.2.0
#> [7] TH.data_1.1-2 tensorA_0.36.2.1 digest_0.6.35
#> [10] estimability_1.5 lifecycle_1.0.4 StanHeaders_2.32.8
#> [13] processx_3.8.4 survival_3.5-8 magrittr_2.0.3
#> [16] compiler_4.4.0 rlang_1.1.4 sass_0.4.9
#> [19] tools_4.4.0 utf8_1.2.4 labeling_0.4.3
#> [22] bridgesampling_1.1-2 pkgbuild_1.4.4 curl_5.2.1
#> [25] plyr_1.8.9 xml2_1.3.6 abind_1.4-5
#> [28] multcomp_1.4-25 withr_3.0.0 grid_4.4.0
#> [31] stats4_4.4.0 fansi_1.0.6 xtable_1.8-4
#> [34] colorspace_2.1-0 inline_0.3.19 emmeans_1.10.1
#> [37] scales_1.3.0 gtools_3.9.5 MASS_7.3-60.2
#> [40] ggridges_0.5.6 cli_3.6.2 mvtnorm_1.2-4
#> [43] generics_0.1.3 RcppParallel_5.1.7 binom_1.1-1.1
#> [46] reshape2_1.4.4 commonmark_1.9.1 rstan_2.32.6
#> [49] stringr_1.5.1 splines_4.4.0 bayesplot_1.11.1
#> [52] matrixStats_1.3.0 brms_2.21.0 vctrs_0.6.5
#> [55] V8_4.4.2 Matrix_1.7-0 sandwich_3.1-0
#> [58] jsonlite_1.8.8 callr_3.7.6 arrayhelpers_1.1-0
#> [61] ggdist_3.3.2 glue_1.7.0 ps_1.7.6
#> [64] codetools_0.2-20 distributional_0.4.0 stringi_1.8.4
#> [67] gtable_0.3.5 QuickJSR_1.1.3 munsell_0.5.1
#> [70] tibble_3.2.1 pillar_1.9.0 htmltools_0.5.8.1
#> [73] Brobdingnag_1.2-9 TMB_1.9.11 R6_2.5.1
#> [76] Rdpack_2.6 evaluate_0.23 lattice_0.22-6
#> [79] highr_0.10 markdown_1.12 cards_0.1.0.9046
#> [82] rbibutils_2.2.16 backports_1.4.1 trialr_0.1.6
#> [85] rstantools_2.4.0 Rcpp_1.0.12 coda_0.19-4.1
#> [88] gridExtra_2.3 nlme_3.1-164 checkmate_2.3.1
#> [91] xfun_0.43 zoo_1.8-12 pkgconfig_2.0.3